
Blockchain
What the hell is this blockchain that everyone is talking about?
The blockchain, or chain of blocksת originally designates the data structure used by Bitcoin to list all the transactions carried out by its users since its inception: the transactions are grouped into blocks chained together, and blocks are added to the chain over time. This ledger is shared between members of a network, hence the fact that it is sometimes referred to as a distributed ledger.
Since 2015, blockchain has also been referred to as the decentralized consensus technology brought up to date by Bitcoin. This technology, therefore, designates all the methods allowing the participants of a distributed network to come to an agreement without resorting to a trusted third party. In this article, we explain the blockchain for dummies so that you can understand everything about this “revolution”.

Where does blockchain come from?
The concept of blockchain as we know it today was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto and described in the Bitcoin white paper on October 31, 2008. Satoshi Nakamoto did not coin the term, however, and we owe it to Hal Finney, who first used it in his November 7, 2008 reply to Satoshi to refer to Bitcoin’s proof-of-work chain. He then spelled it ” Block Chain “, in two words. The term was later picked up by Satoshi in the Bitcoin version 0.1 source code, and it gradually became popular within the community.
However, the technology behind the blockchain was not entirely created with Bitcoin and the elements that compose it are much older than we think: the blockchain is indeed the fruit of many years of research in economics, computer science, and cryptography.
Blockchain promotes the idea of decentralization, which, unsurprisingly, opposes centralization. Today we live in a world where the majority of things around us are centralized. They are governed by States, banks, large companies… We trust them, or not, but we cannot do without them. These actors to whom we refer are what are called trusted third parties. The blockchain, on the other hand, operates without a central authority.
Bitcoin, which uses blockchain technology, makes it possible to dispense with trusted third parties for the transmission of value between two entities. This is the first concrete application of this technology. It is now possible, thanks to Bitcoin and the blockchain, to transfer value over the internet between two entities without an intermediary.
It was much more complicated before.
For example, if you send a file to a friend on the Internet, the latter is duplicated. You have a copy of the file and so does your friend: the file is not unique. The file doesn’t go from point A to point B. It stays at point A and a copy appears at point B. So it can’t work for currency. When you give your baker 1 euro to buy a baguette, a copy of the piece does not stay in your pocket. The piece is not duplicated, it is unique, it leaves your wallet to go into the baker’s cash register.
It was therefore impossible to use the existing value transfer systems on the Internet in the context of setting up a monetary system on the Web. The currency would have lost value because with each exchange it would have been duplicated. The whole difficulty was therefore to succeed in creating a currency on the internet that could work as in everyday life.
Thanks to Bitcoin, this is now possible. A functional, reliable monetary system without trusted third parties has emerged.
We will see many other blockchain applications in this article, and you will also find them in many other articles on our site.
Before going any further, we must not forget that the blockchain was originally only a component of Bitcoin. Keep that in mind 🙂
What is Blockchain?
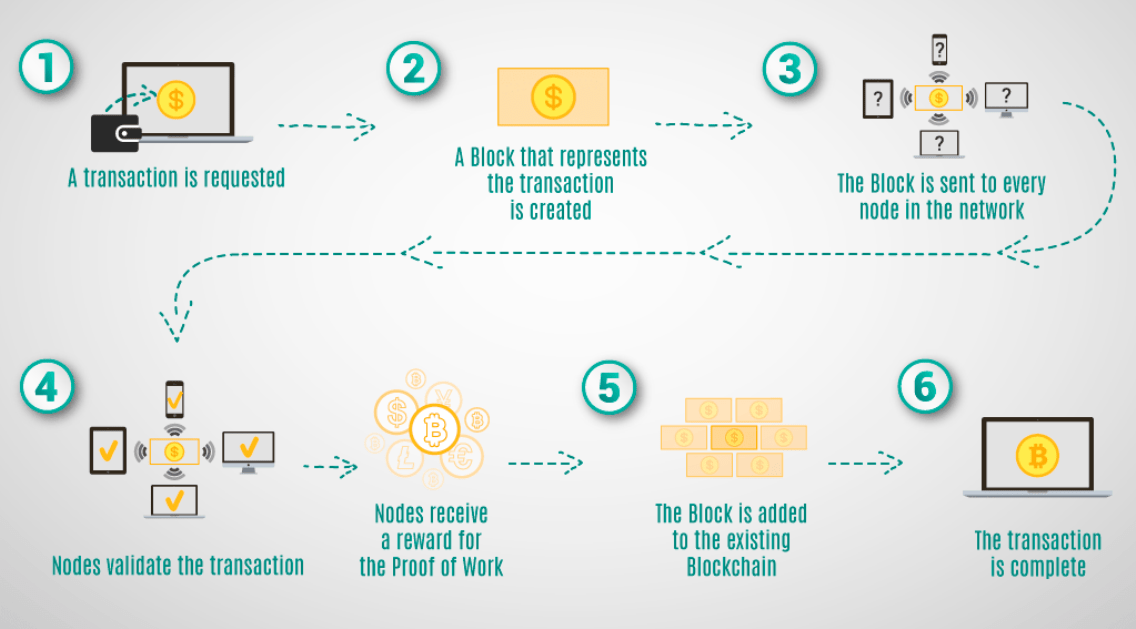
The blockchain, or chain of blocks, can be compared to a digital ledger which is maintained by a network of computers. Data is then added to this ledger in real-time and is visible to all participants.
When a transaction is made on the blockchain, it is added to a block. This block contains all transactions that have taken place in the last few minutes (10 minutes for the Bitcoin network) and have been shared with the entire network of computers.
Network participants are known as nodes. Some of these nodes participate in the verification of the register: they are the validators. Different protocols exist in order to secure the blockchain which will influence the name given to these validators: they will thus be called minors in the event that the blockchain uses proof of work (or proof-of-work in English) or forgers in the case where the blockchain uses proof-of-stake. To learn more about this, see our article on the differences between proof of work and proof of stake. In order to simplify things, we will focus here on proof of work and therefore minors.
Do not confuse miners with blockchain users.
In the case of Bitcoin, miners compete to solve “ cryptographic puzzles ” which help validate transactions. The first miner to solve the riddle receives a reward for his work which, let us remember, allows the security and maintenance of the network. The puzzle is extremely difficult to solve and this difficulty increases over time. Thus, miners must use powerful computers to solve these calculations.
The validation of transactions corresponds to their inclusion and timestamp within a block. This will then make it possible to link the newly validated blocks to old validated blocks. A chain of blocks is formed containing each transaction carried out on the blockchain.
This channel is updated and is accessible to all members of the network. The resulting decentralization allows total transparency and immutability. Thus, everyone has the opportunity to view the data available on the blockchain network.
Resources:
Blockchain is a system of recording information in a way that makes it difficult or impossible to change, hack, or cheat the system. A blockchain is essentially a digital ledger of transactions that is duplicated and distributed across the entire network of computer systems on the blockchain.
By spreading its operations across a network of computers, blockchain allows Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies to operate without the need for a central authority. This not only reduces risk but also eliminates many of the processing and transaction fees.
Blockchain is the technology that enables the existence of cryptocurrency (among other things). Bitcoin is the name of the best-known cryptocurrency, the one for which blockchain technology was invented.
If you believe in blockchain technology, cryptocurrency is a great long-term investment. Bitcoin is seen as a store of value, and some people think Bitcoin can replace gold in the future. Ethereum, the 2nd largest cryptocurrency by market cap, also has huge growth potential as a long-term investment.
Blockchain is already used to facilitate identity management, smart contracts, supply chain analysis, and much more.
One of the notable weaknesses of blockchain is scalability, while blockchain is not indestructible. The anonymous and open nature of blockchains is not an asset, and proof of work is overkill. Lastly, blockchain can lead to complexity, and it can also be horribly inefficient.
Blockchain companies also make money by signing contract agreements with other companies. They make contracts with other companies to provide blockchain infrastructure by designing and developing blockchain applications. They also host the service for a certain period by signing a contract.
The main purpose of a cryptocurrency coin is to function as digital cash. Cryptocurrency coins have their own native blockchain, for example, Bitcoin (BTC), Monero (XMR), and Bitcoin Cash (BCH).
